
Access the admin panel of the router located at the IP address 192.168.0.1. To enter the panel, click Login. (192.168.o.1)
This IP address can be confused with the search for 192.168.o.1.
192.168.0.1 – Access credentials
Access to the panel site is restricted to duly authenticated users, therefore all configuration made on your local network is done from the access point to your network, which in particular is your modem.
To access the general settings, you could use one of the following default usernames and passwords:
- User names: admin and no password.
- Known passwords: admin, password.
As the default user names and passwords have been established by the modem manufacturer, you can use this configuration when it has not been modified by your Internet provider, or if you reset your router to factory mode.
If your modem password has been changed by your Internet provider, you may need to call their technical support number to get the access credentials to 192.168.0.1.
Customize settings

The configuration of your modem or router is very important, especially to improve the level of security and performance of your network, regardless of the modem model, there are many configurations that are customizable.
Customizable settings include the following:
- Device filtering policies: Filtering policies are firewall rules that regulate incoming and outgoing traffic to devices.
- It is the first measure of defense against attacks directed towards the server or internal devices of the network.
- Internal network monitoring: Any network connectivity problem, or local network error is easily detectable through the network auditing tools that are provided by the modem manufacturer through the panel.
- Device control: Internal network devices may require time or use control because they are part of a company, institution or home, and require use restrictions.
- Router password change: The router username and password can also be customized to access the 192.168.0.1 panel or also access the internet.
- The username is also called the SSID, and the password is WEP key, WPA, or WPA2, depending on the router model and configuration.
192.168.o.1 – Problem solving
Failure to access 192.168.0.1, internet failures or local network connectivity failures are some of the common problems that must be resolved within the network.
Here is a list of the most common problems that exist regarding the configuration in your router.
Connectivity failure to access point
Lack of connectivity to the access point is a major headache for some. A connectivity failure can be due to different causes related to communication with the router.
Normally, connectivity failures are not permanent, and here are some causes of failure, so that you can easily detect them:
- Site connection error: Access to 192.168.o.1 may totally fail or be interrupted. Some common causes are as follows:
- Ethernet error: When the connection is made via cable, an ethernet error occurs when there is no packet forwarding over the network.
- The solution in this case would be to check the physical connection of the device with the router, see that it is correctly connected.
- WiFi error: The device is not connected to the WiFi network or is connected to a different network.
- The solution is to verify that the device has WiFi turned on and that it is connected to the same SSID network.
- Admin panel is not in 192.168.0.1: It is possible that your router is not Netgear or DLink, if this is the case, you could access the router’s administration panel using another local IP address, for example: 192.168.1.254.
- Spelling error: If the user enters an unknown IP address, out of range or text strings that are not IP addresses (for example 192.168.o.1), they will not have access to the configuration panel.
- Ethernet error: When the connection is made via cable, an ethernet error occurs when there is no packet forwarding over the network.
Login failed at 192.168.0.1
If you managed to enter the login window, but you do not have access to the panel, this section is indicated to help you solve your access problem.
If after a few authentication attempts you are unable to enter the access point settings, you may need to verify your credentials. Some of the most common causes of access failure in user authentication at 192.168.0.1 are the following:
- Wrong credentials: If your username or password are not correct, obviously you will not have access. To do this, check with your ISP or provider for the access credentials or try to enter using the factory credentials.
- You may have to reset your modem to factory mode, the process to do it is by pressing the small hole on the side of your modem for a few seconds.
- Lack of privileges: Maybe your access point contains several users, if there are some who do not have administrator permissions, they may not have access to the configuration change features within your panel. Always log in with an administrator user.
192.168.o.1: Write errors
Even if indirect access, or through Google, Yandex, Bing or another search engine, can be accessed with the 192.168.o.1 search, this is a typing error and cannot be accessed directly with that search from the browser.
Some of the most frequent errors made by users when trying to access the site through the search engine are the following:
- 192.168.0.l, 192.168.o.1, 192.168.01, 192.168.1, 192.168.o.1.1, 192.168.l.1, 192.168.1., 192.168.11, 192.168.l.0, 192.168.o, 192.168 o 0.1, 192.168.l.0.1, 192.168.0., 192.168.0.1.1, 192.168.., 192.168, 192., 192, among many other wrong ways.
- Access using a different protocol: Therefore the use of another protocol or link, are wrong ways to access.
External problems
Problems that are not directly related to your internal configuration, but that affect your services, are known as external problems.
Entering 192.168.0.1 and not having internet access is a known form of an external problem. The most common external problems of a network are the following:
Errors of ADSL
The ADSL or telephone line is the communication transmission medium for your wired internet service. A user could face internet connection problems when DSL service is not working properly, including frequent service interruptions.
The problem occurs even when there is a successful connection to the panel website, since the problem is not in your local network, but in the connection of the modem with the telephone line.
Some of the most common causes are as follows:
- Failures outside the service: These are those presented by some repair or failure in a sector outside your home, for example a cut in the internet wiring in your neighborhood, failure or repair in a box, or in the relay station.
- Generally the failure is temporary, and requires action by the technicians externally, reporting the problem will be sufficient.
- Internal failures: Your service installation has coverage failures, redundancy or faulty wiring. A technician should come to your home to investigate the cause and repair it.
- Faulty modem: If your modem fails, it can also be a problem because of the absence of internet, the panel will say DSL connection failure or you could even have problems accessing the configuration panel.
- The solution is the replacement of the modem with your provider.
Address range 192.168.0.1
The preset range of network addresses marks a set of possible addresses to be assigned in each of the devices located within the local network. Each of these devices has an IP address within that range.
The range is determined by means of the netmask (or network mask). The address can be assigned in a fixed or dynamic way, through a DHCP mechanism, which works for any operating system.
In the case of the access point located at the IP address 192.168.0.1, the normal range of addresses goes from that address to 192.168.0.255, without considering the reserved addresses, 192.168.0.255 for broadcast and 192.168.o.1 for the access point. . This range is compatible with the 255.255.255.0 netmask.
So technically devices within the local network have an IP address in the range 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.254, regardless of whether they are assigned statically or dynamically.
Addresses IPv4
IPv4 addresses are the set of IP addresses for protocol version 4. This protocol version is specified in RFC 1918 (Request For Comments), on the assignment of IP addresses, and so far it is one of the network protocols most accepted worldwide.
The specified range for IPv4 addresses is from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255, where 192.168.0.1 belongs to the set of IPv4 addresses.
In addition, IPv4 addresses are classified into public IP addresses, which are addresses assigned by the IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) for public use and private IP addresses, which are assigned for private use, that is, exclusively within a local network.
The range of private IP addresses is very limited compared to the range of public IPv4 addresses. The defined range is as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255: Class A, with a total of 16,777,214 private IP addresses for each network.
- 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255: Class B, with a total of 1,048,576 addresses, of which 65,534 can be assigned by each network.
- 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255: Class C, with a total of 65,534 IP addresses, with 254 possible IP addresses for each network.
- 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255: Class B, with a total of 65,534 assignable addresses for each network.
So we can see that IP address is located in class C, and for that reason it is possible to assign 254 IP addresses in this assigned range for devices on the local network.
Check connectivity to access point 192.168.0.1
To check if there is successful connectivity in the access point, it is very simple using the ping tool.
The ping tool is responsible for sending short network packets under the ICMP protocol to see if there is a pong response from the server. Its operation is as seen in the ping pong game: it sends a packet to the target, and calculates the response reception time.
In this particular example, if the access point is active, there must be a response when executing the command in the console:
ping 192.168.0.1
In this particular example, if the access point is active, there must be a response when executing the command in the console:
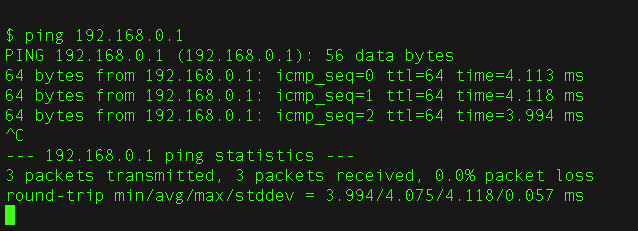
Note: When the connection fails, the ping will result in a timeout, so we could verify what the IP address of the access point is using the ifconfig command.
We take as a reference the network value that is indicated in broadcast, which gives us a clue of the value in which our access point could be located.
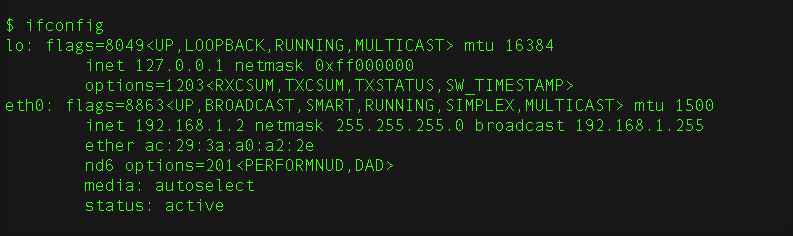
In the example we show two interfaces: localhost, with IP address 127.0.0.1 and eth0, with IP address 192.168.1.2, as the broadcast shows 192.168.1.255, the access point could be 192.168.1.254, therefore we ping to 192.168.1.254 to see if there is a response:
ping 192.168.1.254
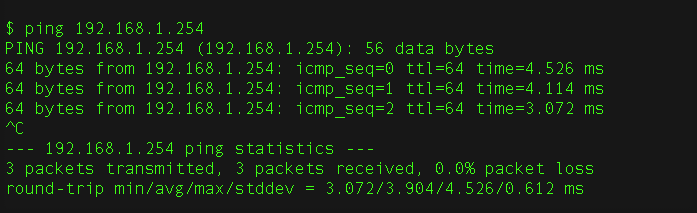
And since we see that there is a response from 192.168.1.254, we deduce that this is the access point, as long as none of our other devices connected to the network have such an IP address assigned.
What is the IP address of my gateway? Some known broadcast values with probable IP addresses are as follows:
- 192.168.0.255: Access point is located at 192.168.0.1
- 192.168.1.255: Access point located at 192.168.1.254
- 192.168.100.255: Access point located at 192.168.100.1
- 192.168.10.255: Access point located at 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.8.255: Access point located at 192.168.8.1
Conclusions
The access point located at 192.168.o.1 allows you to modify your network configuration, for example, your network password, firewall rules, intrusion blocking, among other functions such as monitoring your network.
Devices connected on the network receive their IP address statically, or dynamically, as long as the IP address is within the range of the network.
Also in the administration panel you will be able to verify some connection problems of your network, both internally and between the connected devices of the network.
Your internet provider is the first resource to know the username and password of your network at 192.168.0.1, however, if it is not possible to locate it, or you cannot contact technical support, you could consider resetting your modem to factory mode .
Your access point or modem can also fail as it nears the end of its life. Therefore, it is possible that your internet provider will replace it when it begins to fail.